Oculomotor Nerves Are Responsible for Which of the Following Functions
Which division of the nervous system has short preganglionic neurons. Somatic and Autonomic motor function.
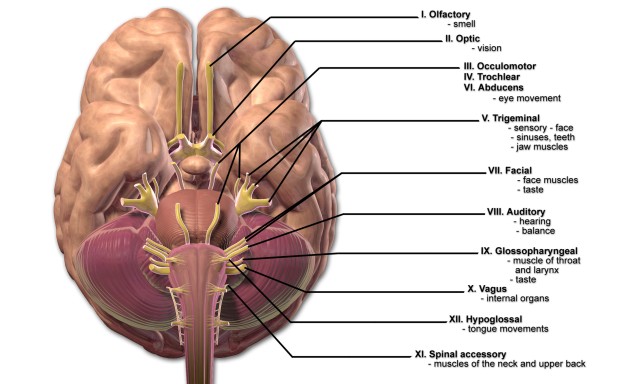
The 12 Cranial Nerves And Their Functions Medical Library
Cranial nerve III works with other cranial nerves to control eye movements and support sensory functioning.

. The oculomotor nerve is responsible for the nerve supply to muscles around the eye including the upper eyelid muscle which raises the eyelid. Oculomotor nerves are responsible for which of the following functions. The oculomotor nerve is responsible for the majority of eye and eyelid movements although the trochlear nerve and abducens nerve also contribute to eye movements.
The oculomotor nerve is entirely motor It is responsible for lifting the upper eyelid. These nerves are paired and present on both sides of the body. The extraocular muscle which moves the eye inward.
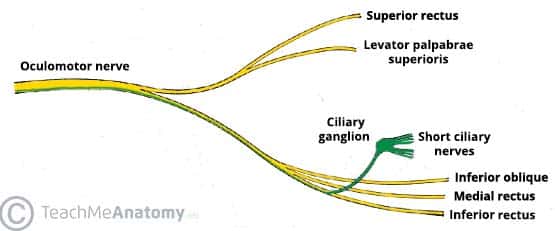
There are 12 cranial nerves that control motor and sensory processes of the head and neck. And the pupillary muscle which constricts the pupil. The constrictor pupillae of the iris and the ciliary muscles are supplied by the parasympathetic component of the oculomotor nerve These fibers synapse in the ciliary ganglion and reach the eyeball in the short ciliary nerves.
The third cranial nerve. These functions of eye movement occur through innervation of four eye muscles. Cranial nerves arise directly from the brain in contrast to spinal nerves and exit through its foramina.
Parasympathetic ganglia are also called what because of their location. The intrinsic muscles of the eye. Sensory nerves are those nerves which carry the stimulus from the effector organs to the brain which is further processed to generate a specific response.
The oculomotor nerve controls the muscles that regulate all eye movements except moving the eyeball down or outward. Which cranial nerve is responsible for movement of the eye laterally. Oculomotor nerves are responsible for which of the following functions.
What is the function of Oculomotor Nerve III. Olfactory receptors are responsible for the detection of odour. SO 1416 Identify the origin of the vagus X nerve in the brain the foramen through which it exits the skull and its function.
Somatic voluntary functions of the oculomotor nerve include elevation of the upper eyelid via innervation of the levator palpebrae superioris muscle. Determine which of the following is the oculomotor nerves function. Optic receptors are responsible for vision.
The cerebellum performs all of the following functions except. Other essential functions include coordination of eye muscles for visual tracking and gaze fixation. Turning the eye upward.
This nerves nucleus is made up of many small nuclei that are divided. Optic abducens trigeminal accessory. Cranial nerves are concerned with the head neck and other facial regions of the body.
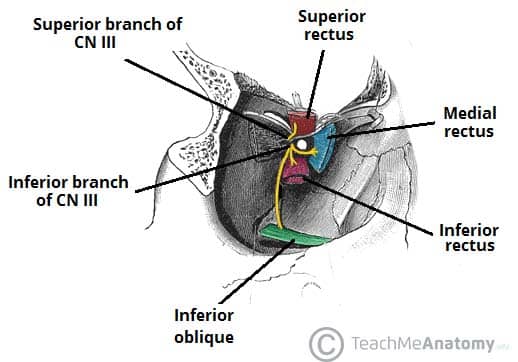
Eye movement Superior inferior medial rectus muscles and inferior oblique muscle opening of eyelid levator palpebrae superioris constriction of pupil circular muscle focusing ciliary muscle and accomodation Damage causes drooping eyelid dilated pupil double vision. The oculomotor nerve is the third cranial nerve CN III. A Oculomotor b Trigeminal c Spinal accessory d Facial e.
A Focusing the eyes on close objects b Activating the parotid salivary glands c Activating the nasal and lacrimal glands of the eyes d Reflexive blinking of the eyes. Exhibit 14H Vagus X Nerve 41 Which of the following cranial nerves is primarily responsible for changing facial expressions. Move the eye inferiorly and laterally Conduct impulses for vision Pupillary constriction Abduct the eye Reset Zoom.
The oculomotor nerve is the third cranial nerve CN III and one instance in which the name is a clear indication of the function of the nerve Oculo pertaining to the eye motor producing movement. Medium Study Objective 1. All of the following cranial nerves are classified as having a motor function except.
Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers. They are mainly responsible for facilitating smell vision hearing and movement of muscles. Olfactory nerve CN I enables sense of smell.
It allows movement of the eye muscles constriction of the pupil focusing the eyes and the position of the upper eyelid. Simply from the name then it is easy to know that the oculomotor nerve will innervate muscles that move the eye itself or components of the eye. An oculomotor nerve is the third cranial nerve which stimulates motor functions.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4566/2pduaqj1xIEg30pQghR1yw_6._Abducens_Nerve.png)
Motor Cranial Nerves Anatomy Functions And Components Kenhub

Cranial Nerves The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Sheep Brain External Anatomy Ventral Abducens Nerve Hypoglossal Nerve Dollar Store Christmas Crafts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-141483691-4cc225237a5945f8ab949d936f52c48e.jpg)
Cranial Nerves Anatomy Function And Treatment

Acronym Mnemonics For Remembering 12 Cranial Nerves Studypk Medical School Studying Nursing School Studying Nursing School Survival

Cranial Nerve Palsies Smarty Pance Nerve Palsy Cranial Nerves Sensory Nerves

Know All About Your Cranial Nerves Share With Friends Follow Guru Medical For More Follow Guru Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerves Function Nerve Anatomy

Day 539 Cranial Nerves And Their General Functions Blank One For Studying Too The Mnem Nursing School Notes Medical School Studying Nursing School Survival
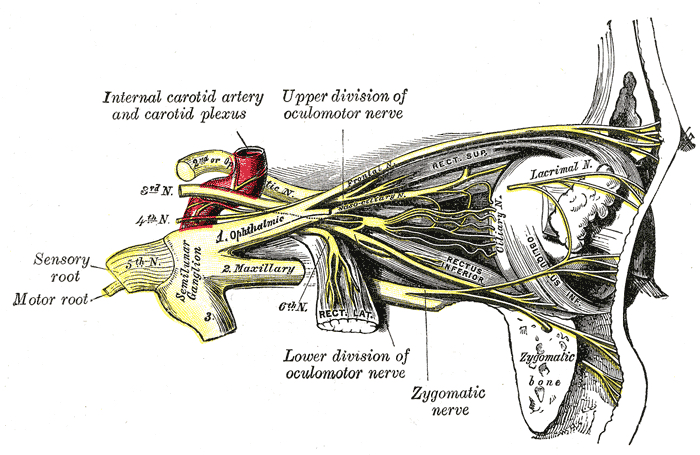
The Oculomotor Nerve Cn Iii Cranial Nerves Anatomy Geeky Medics

Dear Nurses Simplifying The Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerves Craniosacral Therapy Nursing School Tips
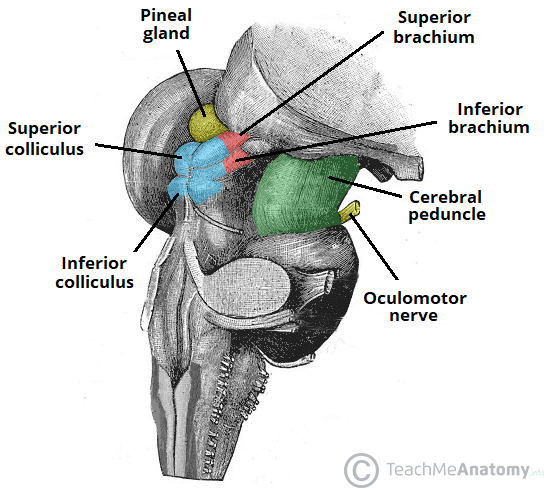
The Oculomotor Nerve Cn Iii Course Motor Teachmeanatomy

Head And Neck Nerves Cranial Classification Functional Overview Dental Hygiene School Dental Anatomy Medical Student Study

Cranial Nerves On Models Labeled Brain Model Somso Nervous System Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology Brain Anatomy

Cranial Nerves Anatomy Nerve Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology

Nursing School Notes Cranial Nerves And Their General Functions Studypk Nursing School Notes Medical School Studying Nursing Students
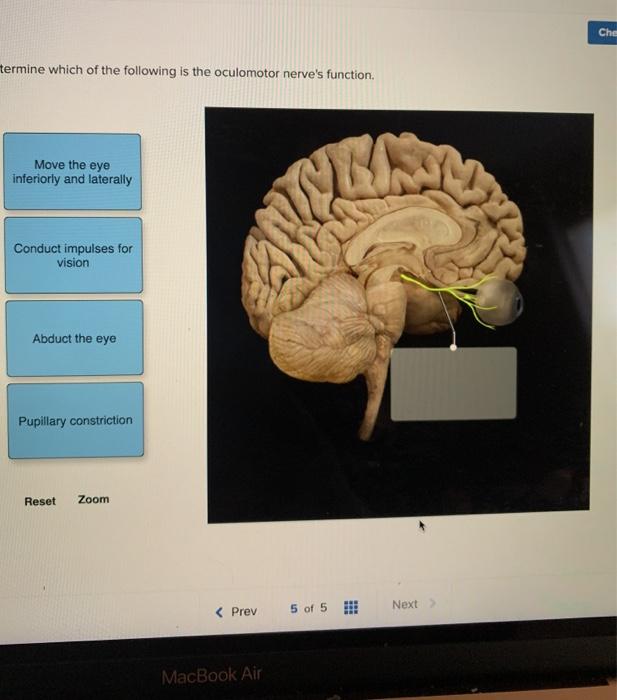
Solved Che Termine Which Of The Following Is The Oculomotor Chegg Com

Comments
Post a Comment